基数排序(经典)
思路分析
介绍:
基数排序是一种非比较型整数排序算法,其原理是将整数按位数切割成不同的数字,然后按每个位数分别比较。由于整数也可以表达字符串(比如名字或日期)和特定格式的浮点数,所以基数排序也不是只能使用于整数。—菜鸟教程
基本思想:
将所有待比较数值统一为同样的数值长度,数位较短的前面补零。然后,从最低位开始,依次进行一次排序。这样从最低位排序一直到最高位排序完成后,数据序列就变有序了。
LSD(最低位优先)基数排序思想↑,另有MSD(最高位优先)实现方式。参考blog。
图解(非常好の图):

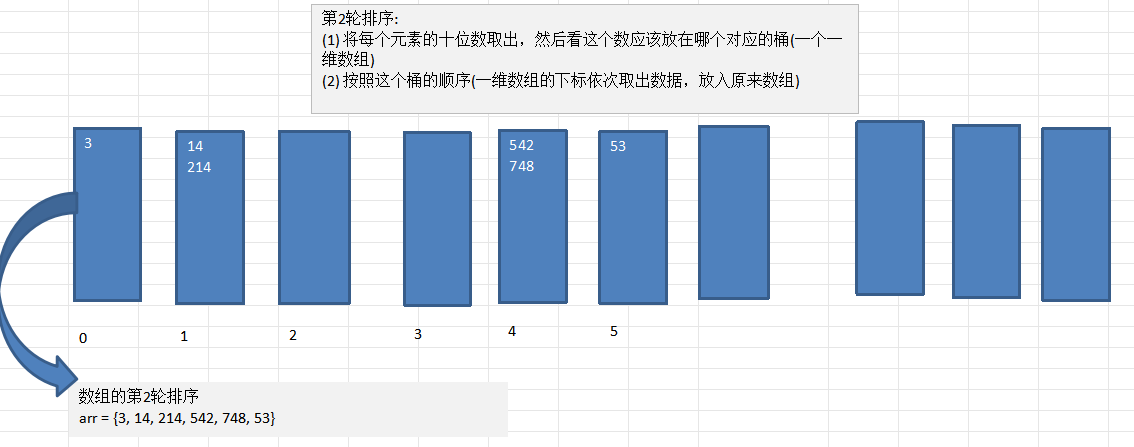

代码思路:
- 关于上面桶如何表示?用一个二维数组
int[][] bucket = new int[10][?],?处要填arr.length,防止数据溢出。
- 所以基数排序就是空间换时间的经典算法。
- 在某轮取数据时,我们怎么知道要从某个桶中取几个数?因此需要有一个方法,告诉我们每个桶中有几个数据。
- 因此定义一个一维数组``,表示每轮10个桶中的有效数据个数。
可以形象地表示为 不断把元素放入桶中,再从桶中取出的过程。这样一放一取要执行maxLength轮(maxLength为最高位数长度)
小结:
速度快+稳定,但是空间耗费巨大。
特别注意:基数排序只适用于正数的情况(问题出在去maxLength那里,不能有负数)。
额外的解决方案6有两个:偏移法或分开处理(正数与负数),可跳转见补充方案详解
代码实现
| 测试数据大小 |
花费时间(单位:毫秒) |
| 10000 |
2 |
| 50000 |
3 |
| 80000 |
10 |
| 140000 |
14 |
| 500000 |
35 |
| 900000 |
35 |
RadixSort
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
| package com.yukinoshita.algorithm.sort;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class RadixSort {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] arr = {53, 3, 542, 748, 14, 214};
System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
radixSort(arr);
System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
testPerformance();
}
private static void radixSort(int[] arr) {
int[][] buckets = new int[10][arr.length];
int[] bucketCounts = new int[10];
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (max < arr[i]) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
int maxLength = (max + "").length();
for (int i = 0, n = 1; i < maxLength; i++, n *= 10) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
int digit = arr[j] / n % 10;
buckets[digit][bucketCounts[digit]] = arr[j];
bucketCounts[digit]++;
}
int index = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < buckets.length; j++) {
if (bucketCounts[j] != 0) {
for (int k = 0; k < bucketCounts[j]; k++) {
arr[index++] = buckets[j][k];
}
bucketCounts[j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
public static void testPerformance() {
int size = 140000;
int[] arr = new int[size];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] = random.nextInt(100000);
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
radixSort(arr);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("排序大小: " + size);
System.out.println("排序时间: " + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");
}
}
|








